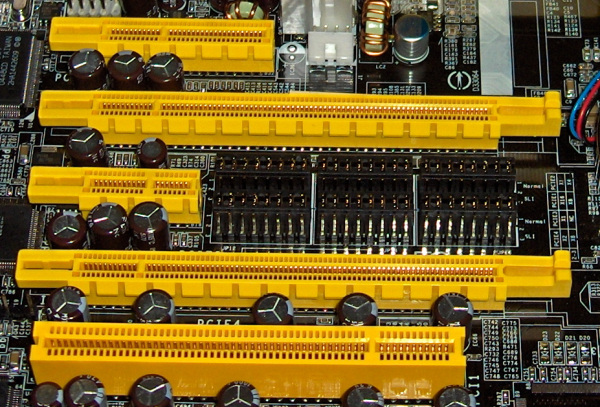
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), universally known as PCIe, is a computer expansion card designed to replace legacy ISA, PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. PCIe offers numerous improvements over ISA, PCI and PCI-X, including higher maximum system bus throughput, lower I/O pin count and smaller physical footprint, better performance-scaling for bus devices, a more detailed error detection and reporting mechanism and native hot plug functionality.
The PCIe standard defines slots and connectors for multiple widths: x1, x4, x8, x16, x32. This allows PCIe to serve both cost-sensitive applications where high throughput is not required, as well as performance-critical applications.
PCI Express has not only replaced AGP as the default interface for graphics cards on new systems, but has also displaced a major portion of the add-in card market. Most sound cards, TV/capture-cards, modems, serial port/USB/Firewire cards, and network/WiFi cards that would have used the conventional PCI in the past have moved to PCI Express x8, x4, or x1.
While a few motherboards still have conventional PCI slots, these are primarily for legacy cards and are being phased out, seeing how operating systems no longer support the older hardware.
The Benefits of PCIe for Industrial PC users:
- Higher maximum system bus throughput
- Lower I/O pin count
- Smaller physical footprint
- Better performance-scaling for bus devices
- More detailed error detection and reporting mechanism
- Native hot plug functionality.
Still have questions? Feel free to post a comment or email me for more information.
